Quickstart With BashSupport Pro
Thank you for using BashSupport Pro!
We hope that this tutorial helps you to get started quickly. Please contact support if you’re stuck or if you don’t know how to use our software.
Installing a JetBrains IDE
BashSupport Pro is an extension for JetBrains IDEs. You have to install such an IDE to use our software. If you’re already using IntelliJ IDEA or any of the other IDEs, then just skip this step.
- Pick an IDE. The easiest way is to select one using the JetBrains product chooser.
- Click the “Download” button next to the IDE of your choice.
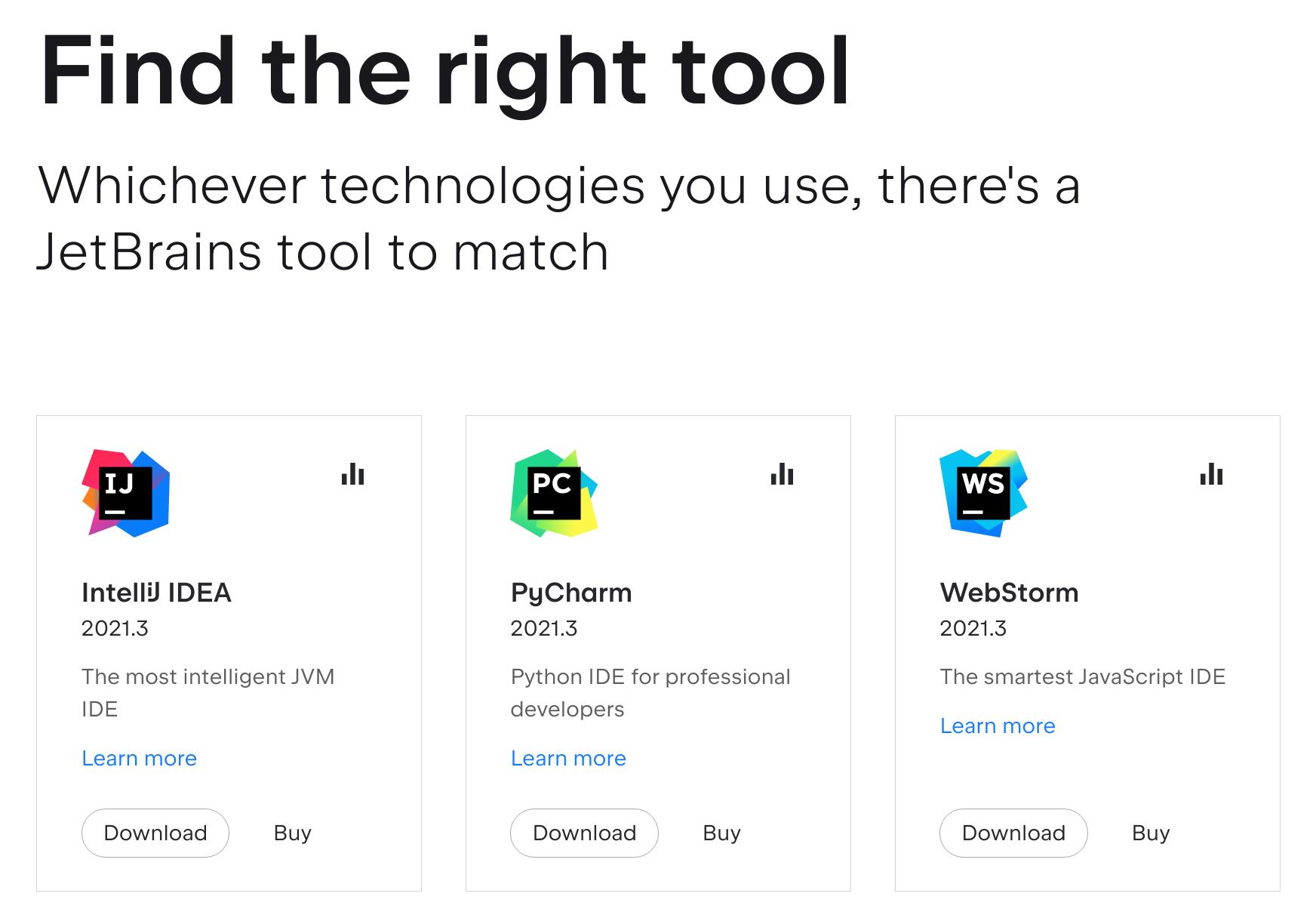
Using the JetBrains product chooser
- Install the IDE on your system. For our tutorial, we’ll use IntelliJ IDEA Community. An alternative way to install it is JetBrains Toolbox. The download page has links to install instructions.
- Launch it. It will now display a wizard to set up your IDE.

IntelliJ IDEA's welcome screen - Click Open and choose an empty directory as a project. In our example, we’ll pick
/bashsupport-projectas directory path.
Choosing an empty project directory - Now, a new window of your IDE will be opened.

IntelliJ IDEA with a new project - Close the dialog about daily tips and other the visible notifications. If your IDE opened a new file for the new project, just close it.
Installing and Configuring BashSupport Pro
You need:
- a JetBrains IDE, version 2022.1 or later
- macOS, Linux or Windows
There are two ways to install the BashSupport Pro Plugin.
Automatic Installation
- Launch your JetBrains IDE
- Click the “Install” button below. Your IDE will prompt you to trust “bashsupport.com”. When you accept a dialog will appear where you confirm to install our plugin.
- Please restart your IDE to activate the new plugin.
Manual Installation
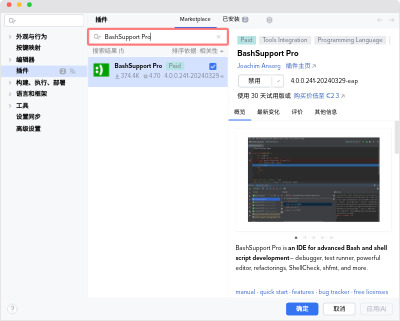
- Choose Preferences… → Plugins → Marketplace.
- Enter “BashSupport Pro” into the search input.
- Click Install next to the “BashSupport Pro”.
- Your IDE may show a message to trust 3rd-party plugins. You need to confirm to continue.
- The Install button changes to Restart IDE
- Click this button to complete the installation of BashSupport Pro.
Activating Your License
BashSupport Pro needs a license. There’s a free 30-day trial license if you’re using it for the first time.
- After the restart, your IDE displays a dialog to enter the license information.

Dialog to activate your license of BashSupport Pro - Choose the license you’d like to activate:
- Activate BashSupport Pro if you’ve already purchased a license
- Start trial to use your free 30-day trial. This is only possible if you’ve not used a trial of the current major version before.
- Click Log In to JetBrains Account… to fetch the license associated with your JetBrains account.
- Click Activate to finish the activation and to close the dialog.
Congratulations, you’ve successfully registered your copy of BashSupport Pro!
Setting Up BashSupport Pro
Now, you should see the main window and a notification to help you set up BashSupport Pro.

Notification to configure BashSupport Pro Click Open Setup to launch the setup wizard. If you don’t see this notification, please use Help → BashSupport Pro Setup.
The first page lists important links and how to get started. Click Next.

Setup wizard of BashSupport Pro Configure the plugins of your IDE.
Most JetBrains IDEs bundle the JetBrains Shell plugin. Because the Shell plugin registers itself for the same file extensions it’s not recommended using both plugins at the time.
Click Next to disable the JetBrains Shell plugin.

Setup wizard of BashSupport Pro Now you can take a few optional steps. If you’d like to receive occasional updates about the plugin please register for the newsletter.
Click Next to apply the information.

Optional setup step of BashSupport Pro If necessary, the final step asks you to restart your IDE. Please Restart to apply all changes. Otherwise, click Finish to close the dialog.

Final setup step of BashSupport Pro
Configuring Your Shell Interpreters
BashSupport Pro detects the installed shell script interpreters on your system. Please make sure that you’ve installed at least one supported Bash interpreter and that it’s properly detected.
- Open the settings at Preferences… → Languages & Frameworks → BashSupport Pro → Shell Interpreters

Interpreter settings - Verify that there’s at least one row with type Bash (.bash) in the table.
- If you don’t see any Bash interpreter, please make sure it’s installed and refresh the table with the “Rescan” action.
- Close this dialog.
Creating Your First Script
Now, we’re ready to create our first shell script file!
- Open the project view, that’s the tool window on the left with title Project.
- Select the top-level directory and open the context menu by right-clicking on the item
- Choose New → Shell Script

How to create your first shell script file - A popup to create the shell script file appears.

Popup to choose the type of your new script - Enter quickstart.bash as filename and press Enter to create the new file.
- Now, the file is created and the editor for it is opened.
You’ll see a popup to let you choose the shebang line.
Just press
Enter
to accept the default value.

Editor showing the new file
Editing Your Script
Our task is to create a function, which takes a number n and prints the sum 1 + 2 + ... + n to STDOUT.
For example, for n=5 the sum of 1+2+3+4+5 is 15.
- Type
func
get the live template for a new function.
If necessary, press
alt →
enter
to see the code completion menu.

Live template to create a new function - Type the name of the new function:
print_sum
.
Press Enter to move the text cursor inside the function. - Press
Enter
once more to confirm the suggested body of the function.

Newly created shell script function - Now, we’re ready to implement this function!
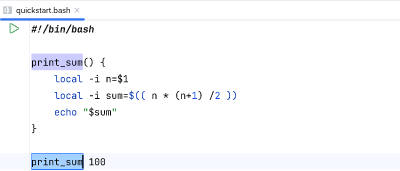
We’re lazy and use the formula for triangular numbers:sum = n * (n + 1) / 2. We’re using an arithmetic expression$(( ))to calculate the result. - Our function now looks like this:

Function to print the sum of 1+2+...+n
Code Completion
Our function is still unused. We’ll use code completion to insert a call of it.
- Add a few empty lines at the end of the file.
- Invoke code completion with
Ctrl →
Space
to show the name of our new function.

Autocompletion of a function name - Press Enter to insert the function call and pass a number as argument.
Renaming Elements
BashSupport Pro helps you to rename variables, functions, and more.
Renaming a Function
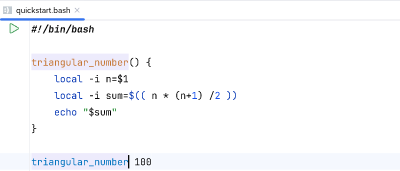
Let’s rename the function print_sum to triangular_number.
To do this, place the text cursor on print_sum.
It doesn’t matter if it’s the name of the definition or the name in the invocation.
Choose Refactor → Rename… to start the rename refactoring.
Enter the new name and confirm your choice with Enter .
Renaming a Variable
Variables are renamed in the same way.
Let’s rename the local variable n to number.
Place the text cursor on n, invoke Refactor → Rename… and enter the new name of the variable.
As you can see, the definition and all references have been updated.
Formatting
The spacing and indentation of our file needs a cleanup. Let’s reformat it!
Invoke Code → Reformat File to choose how to reformat it. Choose Whole file, because that’s supported best.
Confirm your choice with Enter to reformat the file. It now looks like this:

Navigating in Your Script
Go To Definition
Navigate → Declaration or Usages allows you to navigate between references to functions or variables and their definitions.
Let’s practice this with the variable number.
- Place the text cursor on a reference to variable
number.
Navigating from variable reference to definition - Execute Navigate → Declaration or Usages or use the matching keyboard shortcut.
- The text cursor is now at the position, where the variable is defined.

After navigating to a variable definition
Executing Your Script
It’s time to execute our little script!
There are two ways to do this:
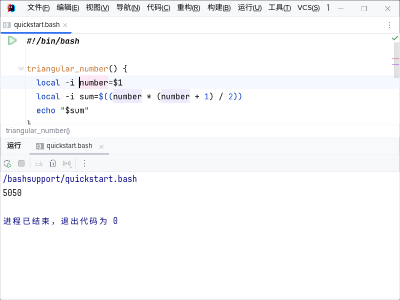
- Run → Run ‘quickstart.bash’

Executing a script using the main menu - The green arrow on the left of the first line of the editor.

Executing a script using a line marker
Execute the script by clicking any of the two items. Tool window Run is now opened and displays the output of the script.
Debugging Your Script
Setting Breakpoints
A breakpoint defines where the execution should pause to let you debug it. You can add a breakpoint by clicking into the empty space left of a line. A red dot signals that a breakpoint is set on a line.
Launching The Debugger
The debugger is launched in almost the same way, just use Debug ‘quickstart’ instead.
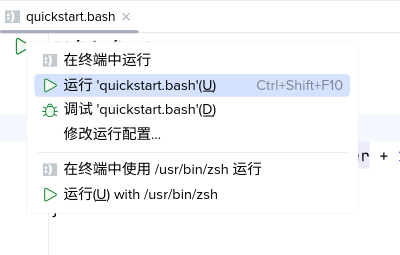
When you launch the debugger, the Debug tool window is shown.
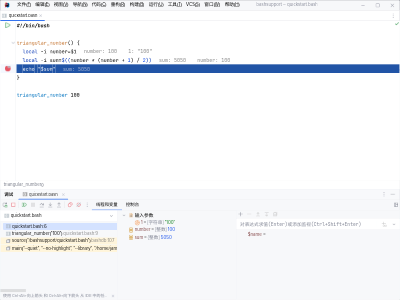
In the tool window, you see the available variables, their current values, and more. Please refer to our documentation about the debugger to learn more about it.
Congratulations!
Thanks for following up to the end!
There’s a lot more of what BashSupport Pro can do:
- Find problems in your scripts: ShellCheck and our own inspections
- Create, edit and execute bats-core tests
- More powerful navigation features
- More refactorings
- Z shell support
- Please refer to our complete documentation to learn more about all the other available features.
Please contact us if you have questions or other feedback about BashSupport Pro.